Serial MultiView: an efficient approach to mitigating atmospheric spatial-structure errors for VLBI astrometry
Jingdong Zhang
It is difficult for VLBI to perfectly correct atmospheric spatial structures, unless a close enough calibrator can be found, e.g., an in-beam calibrator. These errors could lead to lower SNRs and more artifacts for imaging, and position offsets for astrometry, up to milliarcsecond level at centimeter wavelengths.
The new approach introduced in this work, serial MultiView (sMV), detects and corrects phase ambiguities through making use of time-domain information. Assuming residual phases changes continuously, the phase plane should be highly predictable within a short time range, therefore ambiguities can be told apart. A difficulty here is that outliers in measured phase values may cause misjudgments, for which a tree-like traversal is performed to improve robustness.
An example is shown here: a VLBA observation at C band (ID: BZ087B1) with four calibrators around the target. Time series of phases on different baselines are shown in Figure 1. On baseline BR-PT, residual phases are small during the whole session, while on baseline HN-PT (HN low elevation), residual phases change faster and ambiguities occur. The ambiguities are automatically and successfully corrected with sMV, therefore phase corrections at the target’s position can be interpolated.
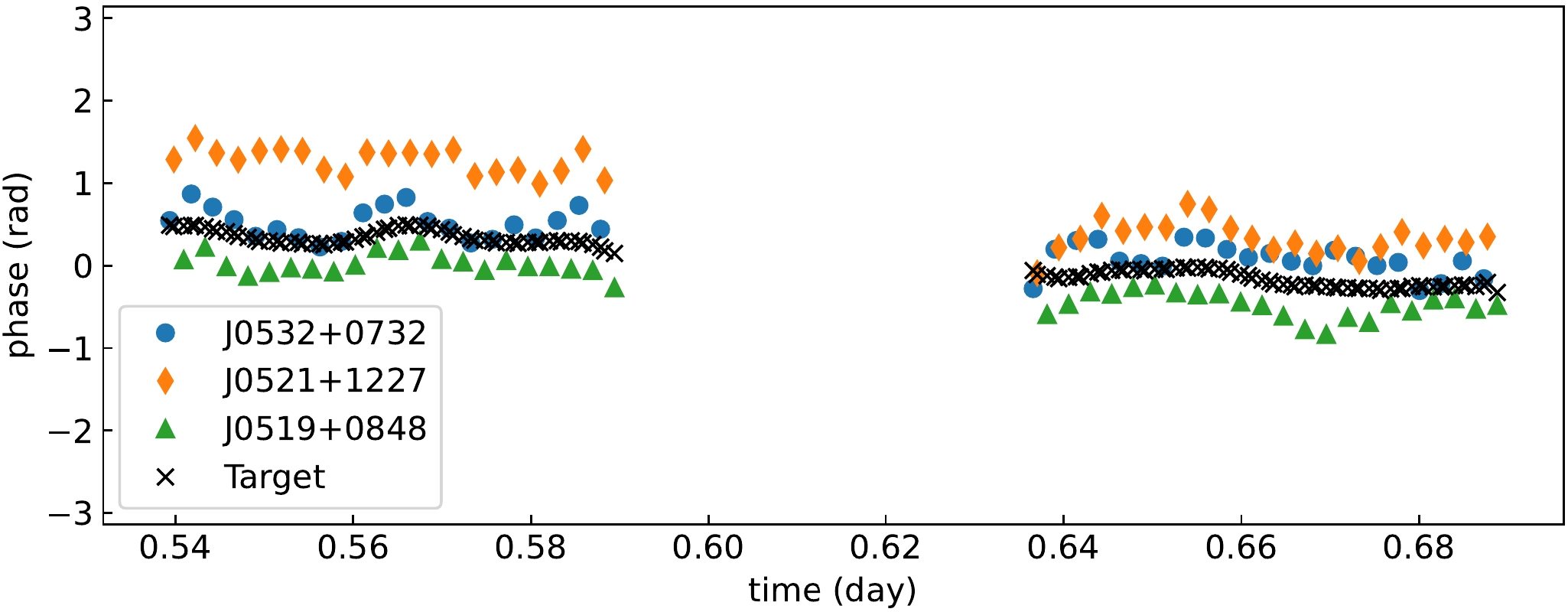
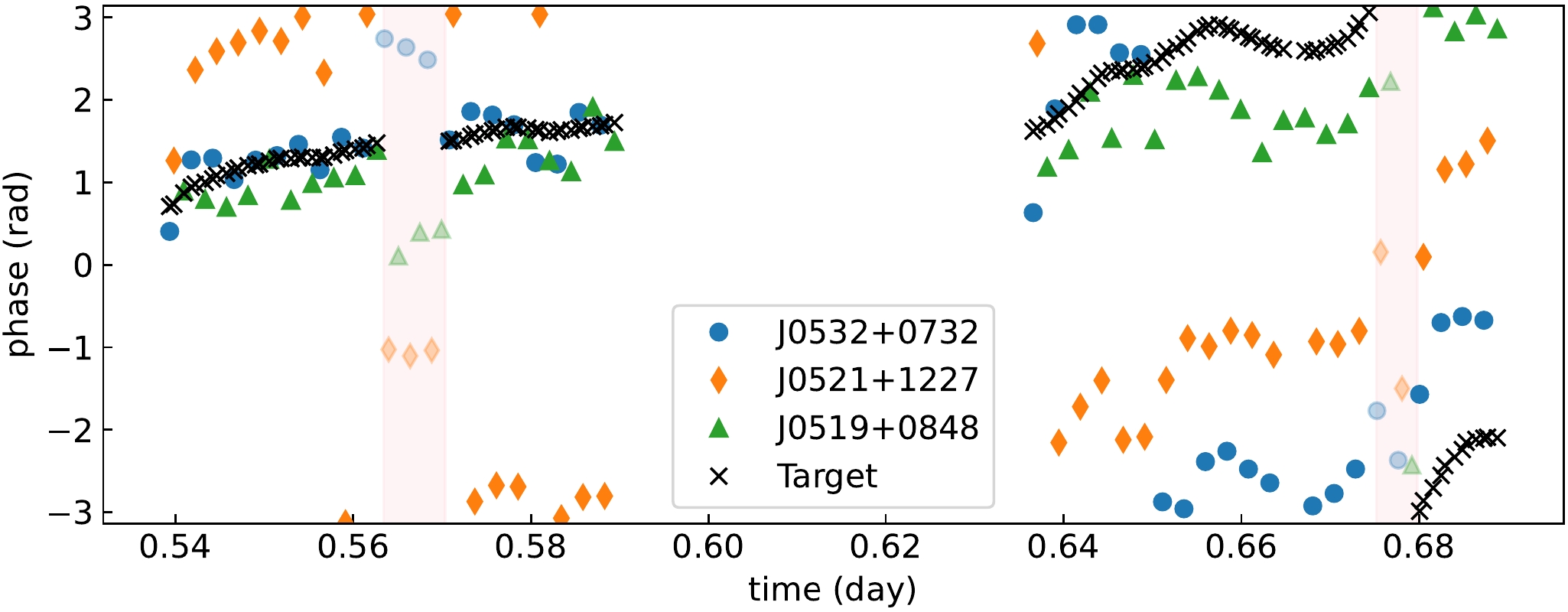
Figure 1. Phases in radians change with time on different baselines. Upper: BR-PT; Lower: HN-PT. Pink backgrounds and semitransparent markers denote being flagged.
Figure 2 shows the imaging result after applying sMV phase corrections, as well as the results of single calibrator phase referencing (PR) and the conventional MultiView (cMV) approach. The same ambiguity corrections as sMV are also applied to the cMV results. In the PR image, many artifacts indicate that the phase is not calibrated well, reducing the imaging quality; while in MultiView images which show high consistency with each other, these artifacts are mitigated, and the improvement in the reconstruction of point-like source significantly contributes to the fitting of the astrometric center.
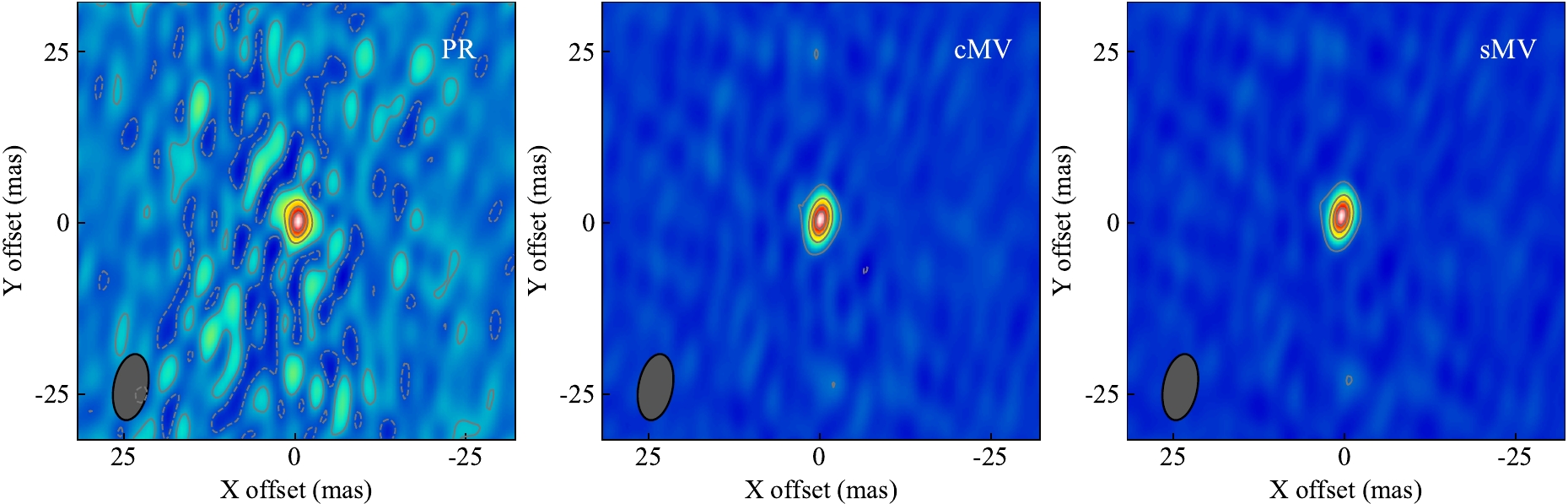
Figure 2. Images calibrated with three techniques. Left: single calibrator PR; Middle: cMV (independent plane fitting) with manual ambiguity correction; Right: sMV with automatic ambiguity correction.
To improve the efficiency and consistency in MultiView data reduction, a pipeline is developed based on AIPS and ParselTongue. A configuration file is used for parameter settings, and some parameters can also be dynamically adjusted as needed. Figure 3 shows the GUI for sMV, which clearly shows how phases change with time and enables manual adjusting and flagging the data. The pipeline now supports basic VLBA data reduction workflow, and its upgrade is still ongoing to support more application scenarios.
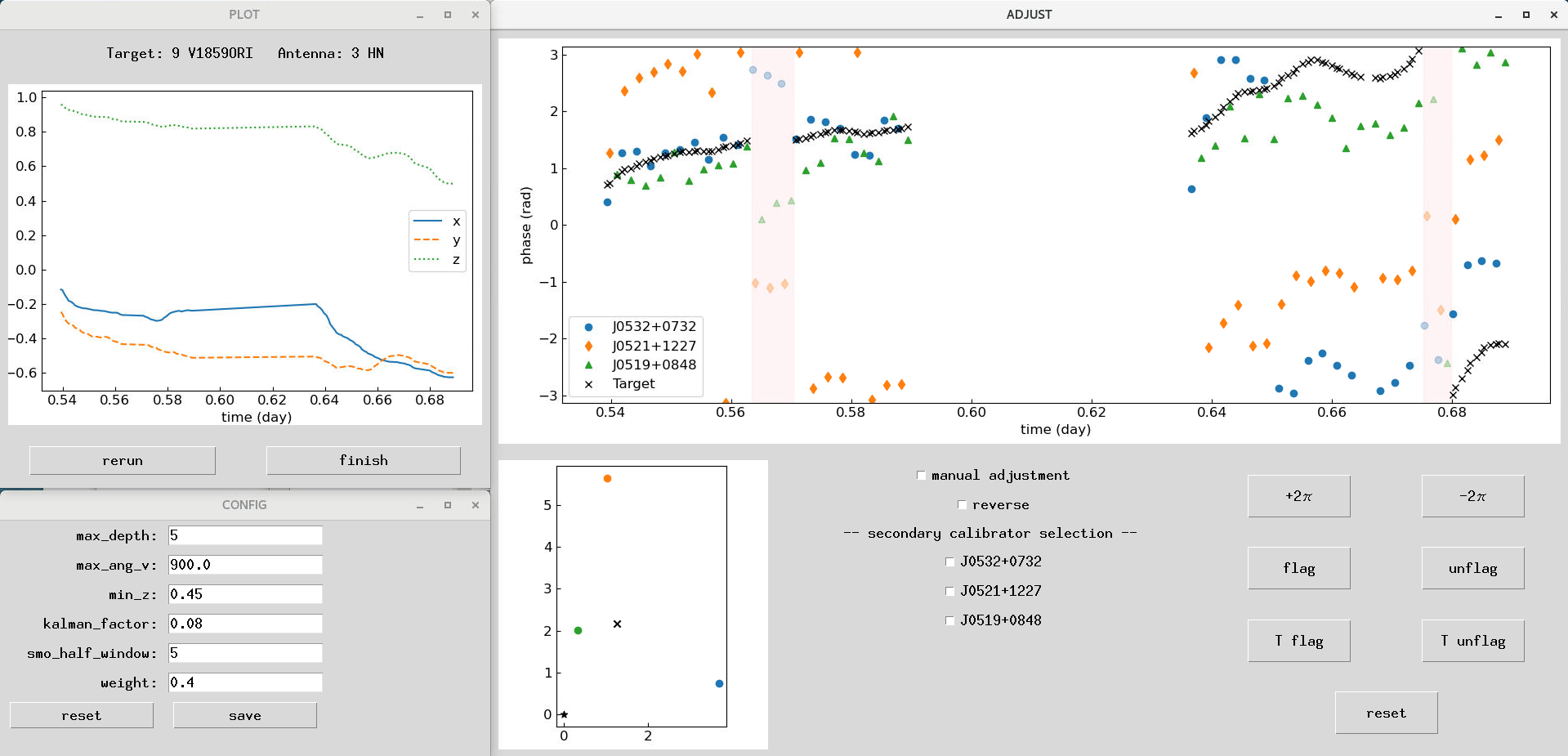
Figure 3. GUI for serial MultiView phase correction in the pipeline. Upper left: normal vector time series plot; Lower left: parameter settings; Right: interactive phase time series plot and manual adjustment panel.
Link to the paper:
Jingdong Zhang et al., 2025, AJ, 170, 4
Contact:
Jingdong Zhang, Shanghai Astronomical Observatory. Email: zhangjingdong@shao.ac.cn
Bo Zhang, Shanghai Astronomical Observatory. Email: zb@shao.ac.cn